Use of form fields
There are a number of form components built into model-form to help you build form forms quickly.
Public methods
Set the value of the form (value)
$form->text('title')->value('text...');Set default values (default)
$form->text('title')->default('text...');Set default (default)This method is only available on add a page, if the edit page also needs to set the default value, you can refer to the following method.
$form->text('xxx')->default('default value', true);Set up a message (help)
$form->text('title')->help('help...');Set attribute
$form->text('title')->attribute(['data-title' => 'title...']);
$form->text('title')->attribute('data-title', 'title...');Set as required
$form->text('title')->required();
// The "*" is not displayed.
$form->text('title')->required(false);Set to uneditable (disable)
$form->text('title')->disable();Setting the placeholder
$form->text('title')->placeholder('Please enter...');Set the width
$form->text('title')->width(8, 2);Set validation rules
See form validation for more details.
Modify form input values to be saved (saving)
The saving method allows you to change the format of the data to be saved.
use Dcat\Admin\Support\Helper;
$form->mutipleFile('files')->saving(function ($paths) {
$paths = Helper::array($paths);
// Get other fields of the current row of the database
$username = $this->username;
// Final conversion to json to save to database
return json_encode($paths);
});Modify form data display (customFormat)
The customFormat method can be used to change the value of a field injected into the form from an external source.
In the following example the mutipleFile field requires that the field values to be rendered be in array format, we can convert the field values from the database to array format by using the customFormat method.
use Dcat\Admin\Support\Helper;
$form->mutipleFile('files')->saving(function ($paths) {
$paths = Helper::array($paths);
return json_encode($paths);
})->customFormat(function ($paths) {
// Get other fields of the current row of the database
$username = $this->username;
// convert to arrays
return Helper::array($paths);
});Hide in pop-ups
If you don't want to display a field in the popup, you can use the Form\Field::hideInDialog method
$form->display('id');
$form->text('title');
$form->textarea('contents')->hideInDialog();Save as string type saveAsString
The saveAsString method converts the form value to a string type for saving, which is useful when the saved database field value is not allowed to be null.
$form->text('nickname')->saveAsString();Save as json type saveAsJson
saveAsJson can save form values in json format
$form->text('nickname')->saveAsJson();Text (text)
$form->text($column, [$label]);
// 添加提交验证规则
$form->text($column, [$label])->rules('required|min:10');Hide field (hidden)
The hidden method allows you to set a hidden field for your form.
$form->hidden('author_id')->value(Admin::user()->getKey());can often be used in conjunction with the saving event
$form->hidden('author_id');
$form->saving(function (Form $form) {
$form->author_id = Admin::user()->getKey();
});Drop-down box radio (select)
$form->select($column[, $label])->options([1 => 'foo', 2 => 'bar', 'val' => 'Option name']);Or get a list of options from api:
$form->select($column[, $label])->options('/api/users');
// Use ajax and display the selected item
$form->select($column[, $label])->options(Model::class)->ajax('/api/users');
// or assign a name and ID
$form->select($column[, $label])->options(Model::class, 'name', 'id')->ajax('/api/users');where the format of the api interface must be in the following format:
[
{
"id": 9,
"text": "xxx"
},
{
"id": 21,
"text": "xxx"
},
...
]If there are too many options, you can dynamically page-load options via ajax:
$form->select('user_id')->options(function ($id) {
$user = User::find($id);
if ($user) {
return [$user->id => $user->name];
}
})->ajax('api/users');To load data during editing using the model method:
$form->select('user_id')->model(User::class, 'id', 'name');The code above is the same as the one below:
$form->select('user_id')->options(function ($id) {
$user = User::find($id);
if ($user) {
return [$user->id => $user->name];
}
});API code for the /admin/api/users interface:
public function users(Request $request)
{
$q = $request->get('q');
return User::where('name', 'like', "%$q%")->paginate(null, ['id', 'name as text']);
}
The data structure returned by the interface is
{
"total": 4,
"per_page": 15,
"current_page": 1,
"last_page": 1,
"next_page_url": null,
"prev_page_url": null,
"from": 1,
"to": 3,
"data": [
{
"id": 9,
"text": "xxx"
},
{
"id": 21,
"text": "xxx"
},
{
"id": 42,
"text": "xxx"
},
{
"id": 48,
"text": "xxx"
}
]
}Drop-down box linkage
The select component supports unidirectional linkage of parent-child relationships.
$form->select('province')->options(...)->load('city', '/api/city');
$form->select('city');
Where load('city', '/api/city'); means that after the current select option is switched, the value of the current option will be taken through the parameter q, calling the interface /api/city, and the data returned by api will be populated into the options of the city selection box, where the format of the data returned by api/api/city must match:
[
{
"id": 9,
"text": "xxx"
},
{
"id": 21,
"text": "xxx"
},
...
]The sample code for controller action is as follows:
public function city(Request $request)
{
$provinceId = $request->get('q');
return ChinaArea::city()->where('parent_id', $provinceId)->get(['id', DB::raw('name as text')]);
}MultiSelect dropdown boxes (multipleSelect)
{tip} The data injected into this field (from the database) can be a string separated by
,, ajsonstring or an array ofarray.
$form->multipleSelect($column[, $label])
->options([1 => 'foo', 2 => 'bar', 'val' => 'Option name'])
->saving(function ($value) {
// Convert to a json string to save to a database
return json_encode($value);
});
// Using ajax and displaying the selected item:
$form->multipleSelect($column[, $label])->options(Model::class)->ajax('ajax_url');
// or assign a name and ID
$form->multipleSelect($column[, $label])->options(Model::class, 'name', 'id')->ajax('ajax_url');The multiple choice box can handle two cases, the first being the ManyToMany relationship
class Post extends Models
{
public function tags()
{
return $this->belongsToMany(Tag::class);
}
}
return Form::make(Post::with('tags'), function (Form $form) {
...
$form->multipleSelect('tags')
->options(Tag::all()->pluck('name', 'id'))
->customFormat(function ($v) {
if (! $v) {
return [];
}
// Converted to IDs from a two-dimensional array of database lookups
return array_column($v, 'id');
});
});
The second is to store an array of options in a single field. If the field is a string, then you need to define accessors and modifiers for the field inside the model to store and read it.
If there are too many options, you can dynamically page-load options via ajax:
$form->select('friends')->options(function ($ids) {
return User::find($ids)->pluck('name', 'id');
})->ajax('api/users');API code for the /admin/api/users interface:
public function users(Request $request)
{
$q = $request->get('q');
return User::where('name', 'like', "%$q%")->paginate(null, ['id', 'name as text']);
}
The data structure returned by the interface is
{
"total": 4,
"per_page": 15,
"current_page": 1,
"last_page": 1,
"next_page_url": null,
"prev_page_url": null,
"from": 1,
"to": 3,
"data": [
{
"id": 9,
"text": "xxx"
},
{
"id": 21,
"text": "xxx"
},
{
"id": 42,
"text": "xxx"
},
{
"id": 48,
"text": "xxx"
}
]
}Table selector (selectTable)
use App\Admin\Renderable\UserTable;
use Dcat\Admin\Models\Administrator;
$form->selectTable($field)
->title('Pop-up window TITLE')
->dialogWidth('50%') // Popup width, default 800px
->from(UserTable::make(['id' => $form->getKey()])) // Set the rendering class instance and pass custom parameters
->model(Administrator::class, 'id', 'name'); // Set the display of editing data
// The above code is equivalent to
$form->selectTable($field)
->from(UserTable::make(['id' => $form->getKey()])) // Set the rendering class instance and pass custom parameters
->options(function ($v) { // Set the display of editing data
if (! $v) {
return [];
}
return Administrator::find($v)->pluck('name', 'id');
});Define the rendering class as follows, which needs to inherit Dcat\Admin\Grid\LazyRenderable.
{tip} The data table is loaded asynchronously, please refer to load asynchronously for more details.
<?php
namespace App\Admin\Renderable;
use Dcat\Admin\Grid;
use Dcat\Admin\Grid\LazyRenderable;
use Dcat\Admin\Models\Administrator;
class UserTable extends LazyRenderable
{
public function grid(): Grid
{
// Getting externally passed parameters
$id = $this->id;
return Grid::make(new Administrator(), function (Grid $grid) {
$grid->column('id');
$grid->column('username');
$grid->column('name');
$grid->column('created_at');
$grid->column('updated_at');
// Specify the field name of the value to be displayed when the line selector is selected.
// Specify the field name of the value to be displayed when the line selector is selected.
// Specify the field name of the value to be displayed when the line selector is selected.
// If the form data has a "name", "title", or "username" field, you do not have to set this.
$grid->rowSelector()->titleColumn('username');
$grid->quickSearch(['id', 'username', 'name']);
$grid->paginate(10);
$grid->disableActions();
$grid->filter(function (Grid\Filter $filter) {
$filter->like('username')->width(4);
$filter->like('name')->width(4);
});
});
}
}result
Multiple Selection (multipleSelectTable)
The usage of multiple choice is the same as the above selectTable method.
$form->multipleSelectTable($field)
->max(10) // 最多选择 10 个选项,不传则不限制
->from(UserTable::make(['id' => $form->getKey()])) // Set the rendering class instance and pass custom parameters
->model(Administrator::class, 'id', 'name') // Set the display of editing data
->saving(function ($v) {
// $v is the value of the form submission field, the default is an array type, here you need to convert it manually.
// Save as a string separated by "," and do not convert if it is a many-to-many relationship.
return implode(',', $v);
});multiple choice box (listbox)
The method is similar to multipleSelect.
{tip} The data injected into this field (from the database) can be a string separated by
,, ajsonstring or an array ofarray.
$form->listbox($column[, $label])->options([1 => 'foo', 2 => 'bar', 'val' => 'Option name']);Long text (textarea)
$form->textarea($column[, $label])->rows(10);Single choice (radio)
$form->radio($column[, $label])->options(['m' => 'Female', 'f'=> 'Male'])->default('m');Multiple choice (checkbox)
options() method is used to set the selection:
$form->checkbox($column[, $label])
->options([1 => 'foo', 2 => 'bar', 'val' => 'Option name'])
->saving(function ($value) {
// Convert to a json string to save to a database
return json_encode($value);
});Enable Select All
$form->checkbox('column')->canCheckAll();Email (email)
$form->email($column[, $label]);Password (password)
$form->password($column[, $label]);Links (url)
$form->url($column[, $label]);IP address (ip)
$form->ip($column[, $label]);Mobile (mobile)
$form->mobile($column[, $label])->options(['mask' => '999 9999 9999']);Color picker (color)
$form->color($column[, $label]);Time (time)
$form->time($column[, $label]);
// Set the time format, see http://momentjs.com/docs/#/displaying/format/ for more formats.
$form->time($column[, $label])->format('HH:mm:ss');Date (date)
$form->date($column[, $label]);
// Set the date format, see http://momentjs.com/docs/#/displaying/format/ for more formats.
$form->date($column[, $label])->format('YYYY-MM-DD');Date and time (datetime)
$form->datetime($column[, $label]);
// Set the date format, see http://momentjs.com/docs/#/displaying/format/ for more formats.
$form->datetime($column[, $label])->format('YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm:ss');timeRange
$startTime and $endTime are the start and end time fields:
$form->timeRange($startTime, $endTime, 'Time Range');Date Range (dateRange)
$startDate and $endDate are the start and end date fields:
$form->dateRange($startDate, $endDate, 'Date Range');time and date range (datetimeRange)
$startDateTime, $endDateTime are the start and end time dates:
$form->datetimeRange($startDateTime, $endDateTime, 'DateTime Range');Scope (range)
$form->range('start_column', 'end_column', '范围');File upload (file)
Before you can use the file upload function, you need to complete the upload configuration first. For file upload configuration and built-in methods, see: Image/File Upload.
The file upload directory is configured in the upload.file file in the config/admin.php file, if the directory does not exist, you need to create the directory and open write permissions.
{tip} Please do not set the accessor and modifier splicing domain name in the file or image upload form fields in the model, refer to File/Image Domain Name Splicing for related requirements.
$form->file($column[, $label]);
// Change the file upload path and file name.
$form->file($column[, $label])->move($dir, $name);
// and set the upload file type.
$form->file($column[, $label])->rules('mimes:doc,docx,xlsx');
// Add file delete button
$form->file($column[, $label])->removable();Image upload (image)
Before using the image upload function, you need to complete the upload configuration first. For image upload configuration and built-in methods, please refer to:image/file upload.
The image upload directory is configured in the file upload.image in the config/admin.php file; if the directory does not exist, it needs to be created with open write permissions.
Compression, cropping, watermarking, etc. can be used in various ways, requiring intervention/image to be installed.
For more information, please refer to [Intervention]:
{tip} Please do not set the accessor and mutator splicing domain name in the file or image upload form fields in the model, refer to File/Image Domain Name Splicing for related requirements.
$form->image($column[, $label]);
// Modify image upload path and file name.
$form->image($column[, $label])->move($dir, $name);
// Cropping pictures
$form->image($column[, $label])->crop(int $width, int $height, [int $x, int $y]);
// Watermarking
$form->image($column[, $label])->insert($watermark, 'center');Multiple Image and multiple file uploads (multipleImage/multipleFile)
Multi-image upload form inherits from single-image upload form, and multi-file upload form inherits from single-file upload form.
{tip} The data injected into this field (from the database) can be a string separated by
,, ajsonstring or an array ofarray
// Multiple pictures
$form->multipleImage($column[, $label]);
// Limit the maximum number of uploads
$form->multipleImage($column[, $label])->limit(3);
// Multiple files
$form->multipleFile($column[, $label]);
// Limit the maximum number of uploads
$form->multipleFile($column[, $label])->limit(5);The data submitted when multiple images/file uploads are an array array, you can change the data to the format you want before saving it into the database by:
// Convert to json format and save to database
$form->multipleFile($column[, $label])->saving(function ($paths) {
// Can be converted to a string format separated by `,`
// return implode(',', $paths);
// can also be converted to json
return json_encode($paths);
});Of course, if you want to save it in any other format, that's fine, it's just that if you want to save it in any other format, you need to convert the data to a one-dimensional array display by using the customFormat method, such as:
$form->multipleFile($column[, $label])
->customFormat(function ($paths) {
return collect($paths)->map(function ($value) {
return explode('|', $value);
})->flatten()->toArray();
})
->saving(function ($paths) {
return implode('|', $paths);
});Enable sortable feature
$form->multipleImage('images')->sortable();Rich Text Editor (editor)
The system integrates the TinyMCE editor as a built-in editor.
Basic Use
$form->editor($column[, $label]);to set up language packs
If you need other languages, you can set the language pack address in the following way:
$form->editor('content')->languageUrl(url('TinyMCE/langs/de.js'));Editor Configuration
For specific configuration, please refer to official document or Chinese document.
<?php
use Dcat\Admin\Support\JavaScript;
$form->editor('content')->options([
'toolbar' => [],
'setup' => JavaScript::make(
<<<JS
function (editor) {
console.log('The editor is initialized with success.', editor)
}
JS
),
]);set height
The default value is 400
$form->editor('content')->height('600');read-only
$form->editor('content')->readOnly();
// 或
$form->editor('content')->disable();image upload
Set the disk configuration for image upload, which is uploaded by default to the configuration specified by admin.upload.disk.
// Upload to oss
$form->editor('content')->disk('oss');Set the image upload directory to tinymce/images by default:
$form->editor('content')->imageDirectory('editor/images');Customize the upload interface, the return format of the interface needs to be {"location": "image url"}.
$form->editor('content')->imageUrl('editor/upload-image');global settings
If you need to set the editor globally, you can add the following code to app\Admin\bootstrap.php.
<?php
use Dcat\Admin\Form\Field\Editor;
Editor::resolving(function (Editor $editor) {
// Setting the default configuration
$editor->options([...]);
// Set the default uploading of editor images to qiniu Cloud.
$editor->disk('qiniu');
});Markdown Editor (markdown)
The system integrates the editor-md editor as a built-in Markdown editor.
Basic Use
$form->markdown($column[, $label]);to set up language packs
If you need other languages, you can set the language pack address in the following way:
$form->markdown('content')->languageUrl(admin_asset('@admin/dcat/plugins/editor-md/languages/zh-tw.js'));Editor Configuration
For specific configuration, please refer to official document
<?php
use Dcat\Admin\Support\JavaScript;
$form->markdown('content')->options([
'onpreviewing' => JavaScript::make(
<<<JS
function() {
// console.log("onpreviewing =>", this, this.id, this.settings);
// on previewing you can custom css .editormd-preview-active
}
JS
),
]);set height
The default value is 500
$form->markdown('content')->height('600');read-only
$form->markdown('content')->readOnly();
// or
$form->markdown('content')->disable();image upload
Set the disk configuration for image upload, which is uploaded by default to the configuration specified by admin.upload.disk
// Upload to oss
$form->markdown('content')->disk('oss');Set the image upload directory to markdown/images by default
$form->markdown('content')->imageDirectory('markdown/images');Customize the upload interface, the return format of the interface needs to be {"success": 1, "url": "image url" }.
$form->markdown('content')->imageUrl('markdown/upload-image');global settings
If you need to set the editor globally, you can add the following code to app\Admin\bootstrap.php.
<?php
use Dcat\Admin\Form\Field\Markdown;
Markdown::resolving(function (Markdown $markdown) {
// Setting the default configuration
$markdown->options([...]);
// Set the default uploading of editor images to qiniu Cloud.
$markdown->disk('qiniu');
});Switch
use
$form->switch($column[, $label]);The default values of the switch form to save to the database are 1 and 0, if you need to change the value to save to the database, you can use this
$form->switch($column[, $label])
->customFormat(function ($v) {
return $v == 'open' ? 1 : 0;
})
->saving(function ($v) {
return $v ? 'open' : 'closed';
});Map (map)
Map control to select latitude and longitude, $latitude, $longitude for the latitude and longitude fields.
To use this feature you need to change the value of map_provider in the config/admin.php file (currently supported maps are: "tencent", "google", "yandex").
For different maps, you need to apply your own KEY and configure it in the .env file, then you need to add the following code to app/Admin/bootstrap.php.
Form\Field\Map::collectAssets();use
$form->map($latitude, $longitude, $label);Slider
Can be used for selection of numeric type fields, such as age.
$form->slider($column[, $label])->options(['max' => 100, 'min' => 1, 'step' => 1, 'postfix' => 'years old']);For more options, please refer to:https://github.com/IonDen/ion.rangeSlider#settings
Display only (display)
Only the fields are displayed and no action is taken:
$form->display($column[, $label]);
// More complex display
$form->display($column[, $label])->with(function ($value) {
return "<img src="$value" />";
});Unit symbol (currency)
$form->currency($column[, $label]);
// Set unit symbols
$form->currency($column[, $label])->symbol('¥');Number (number)
$form->number($column[, $label]);Rating (rate)
$form->rate($column[, $label]);Divider (divider)
$form->divider();Custom content (html)
Insert html content, parameter can be Htmlable, Renderable or a class that implements __toString() method.
$form->html('Your html content', $label = '');Tags (tags)
Insert comma-separated string tags
$form->tags('keywords');tags also supports the relationship ManyToMany, as in the following example.
$form->tags('tags', 'Article Tags')
->pluck('name', 'id') // name is the field of the Tag model to be displayed, id is the primary key.
->options(Tag::all());// drop-down box optionsNote: The pluck method must be called when handling ManyToMany relationships, specifying the field name and primary key to be displayed.
In addition, when the options method is passed to a Collection object, options will automatically call the pluck method of that object to an array of ['Primary Key Name' => 'Show Field Name'] as a drop-down box option. Or you can just use an array like ['Primary Key Name' => 'Show Field Name'] as an argument.
tags also supports the saving method for processing submitted data, as in the following example:
$form->tags('tags', 'Article Tags')
->pluck('name', 'id')
->options(Tag::all())
->saving(function ($value) {
return $value;
});The saving method receives a closure that says "submit value for tags, return value is modified tags submit value" and can be used to automatically create new tags or other features.
If there are too many options, you can dynamically paginate the options via ajax.
$form->tags('friends')->options(function ($ids) {
return User::find((array) $ids)->pluck('name', 'id');
})->ajax('api/users');API /admin/api/users Interface code:
public function users(Request $request)
{
$q = $request->get('q');
return User::where('name', 'like', "%$q%")->paginate(null, ['id', 'name as text']);
}The data structure returned by the interface is
{
"total": 4,
"per_page": 15,
"current_page": 1,
"last_page": 1,
"next_page_url": null,
"prev_page_url": null,
"from": 1,
"to": 3,
"data": [
{
"id": 9,
"text": "xxx"
},
{
"id": 21,
"text": "xxx"
},
{
"id": 42,
"text": "xxx"
},
{
"id": 48,
"text": "xxx"
}
]
}Icon selector (icon)
Select the font-awesome icon
$form->icon('icon');Tree selector (tree)
tree hierarchy form field
$form->tree('permissions')
->nodes(Model::get()->toArray()) // Set all nodes
->customFormat(function ($v) { // Formatting externally injected values
if (!$v) return [];
return array_column($v, 'id');
});
// Modifying the field names of nodes
// Default "id" "name" "parent_id"
$form->tree('permissions')
->nodes($permissionModel->allNodes())
->setIdColumn('id')
->setTitleColumn('title')
->setParentColumn('parent');
// The default is not to save the value of the parent node, since the parent node generally exists only as a TITLE.
// Disable filtering of parent node values
$form->tree('permissions')
->nodes($permissionModel->allNodes())
->exceptParentNode(false);
// Default Collapsed Child Nodes
$form->tree('permissions')
->nodes($permissionModel->allNodes())
->expand(false);Table form (table)
If a field stores a 2D array in JSON format, the table form component can be used for quick editing:
$form->table('extra', function (NestedForm $table) {
$table->text('key');
$table->text('value');
$table->text('desc');
});Also add accessors and modifiers to this field in the model:
public function getExtraAttribute($extra)
{
return array_values(json_decode($extra, true) ?: []);
}
public function setExtraAttribute($extra)
{
$this->attributes['extra'] = json_encode(array_values($extra));
}This component is similar to the hasMany component, but is used to handle the case of a single field for simple two-dimensional data.
One-to-many (hasMany)
A one-to-many inline table for one-to-many relationships is shown in the following simple example.
There are two tables with one-to-many relationships:
CREATE TABLE `demo_painters` (
`id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`username` varchar(255) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci NOT NULL,
`bio` varchar(255) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci NOT NULL,
`created_at` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT '0000-00-00 00:00:00',
`updated_at` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT '0000-00-00 00:00:00',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COLLATE=utf8_unicode_ci;
CREATE TABLE `demo_paintings` (
`id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`painter_id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL,
`title` varchar(255) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci NOT NULL,
`body` text COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci NOT NULL,
`completed_at` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT '0000-00-00 00:00:00',
`created_at` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT '0000-00-00 00:00:00',
`updated_at` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT '0000-00-00 00:00:00',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY painter_id (`painter_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COLLATE=utf8_unicode_ci;The table is modeled as:
<?php
namespace App\Models\Demo;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
class Painter extends Model
{
public function paintings()
{
return $this->hasMany(Painting::class, 'painter_id');
}
}<?php
namespace App\Models\Demo;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
class Painting extends Model
{
protected $fillable = ['title', 'body', 'completed_at'];
public function painter()
{
return $this->belongsTo(Painter::class, 'painter_id');
}
}Build the form code as follows:
use App\Models\Demo\Painter;
// Here you need to explicitly specify the relationship
$builder = Painter::with('paintings');
// If you are using a data warehouse, you can specify the relationships like this
// $repository = new Painter(['paintings']);
return Form::make($builder, function (Form $form) {
$form->display('id', 'ID');
$form->text('username')->rules('required');
$form->textarea('bio')->rules('required');
$form->hasMany('paintings', function (Form\NestedForm $form) {
$form->text('title');
$form->textarea('body');
$form->datetime('completed_at');
});
$form->display('created_at', 'Created At');
$form->display('updated_at', 'Updated At');
// You can also set the label.
// $form->hasMany('paintings', 'paintings', function (Form\NestedForm $form) {
// ...
// });
});result
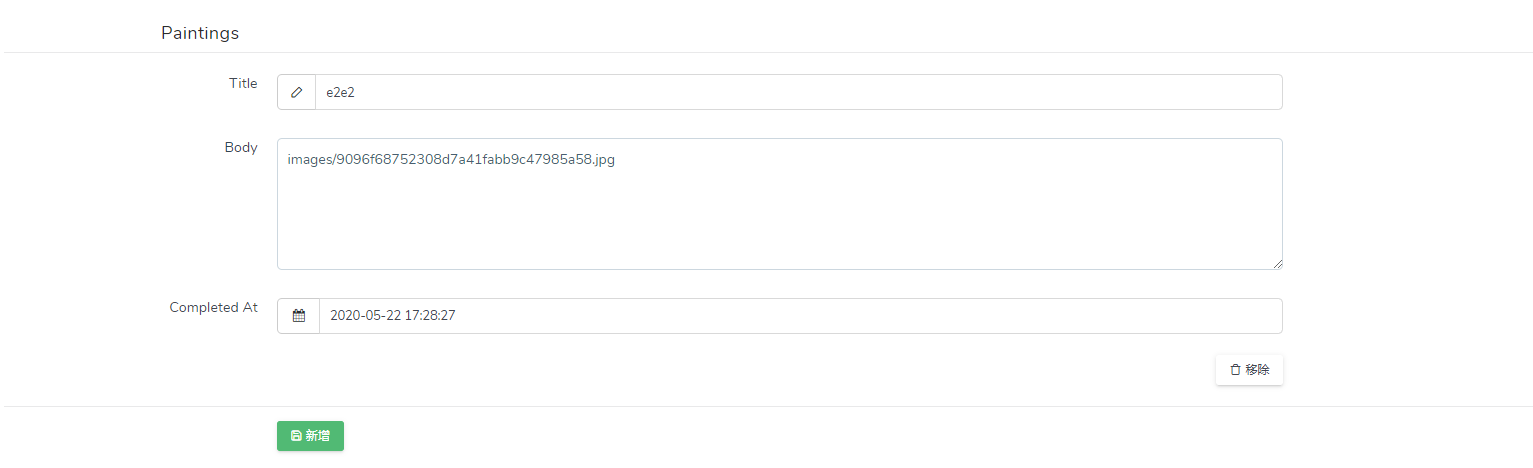
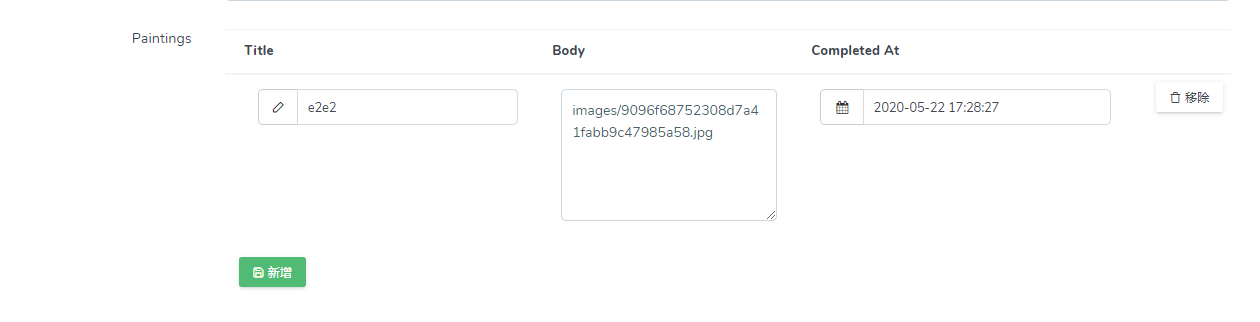
Table schema (table)
If you want to display the table mode, you can use it like this
use Dcat\Admin\Support\Helper;
$form->hasMany('paintings', function (Form\NestedForm $form) {
...
})->useTable();result
Embedded (embeds)
{tip} Embedded forms do not support image and file upload forms.
Used to process mysql's JSON type field data or mongodb's object type data, can also store data values of multiple fields as JSON strings in mysql string type fields.
For example, if the JSON or string type extra field in the orders table is used to store data from multiple fields, define the model first:
class Order extends Model
{
protected $casts = [
'extra' => 'json',
];
}Then in the form use.
$form->embeds('extra', function ($form) {
$form->text('extra1')->rules('required');
$form->email('extra2')->rules('required');
$form->mobile('extra3');
$form->datetime('extra4');
$form->dateRange('extra5', 'extra6', 'Range')->rules('required');
});
// Custom TITLE
$form->embeds('extra', 'Additional information', function ($form) {
...
});The method calls for building form elements inside the callback function are the same as outside.
