Quick start
In daily development, we can use the code generator to generate a key to add, delete and check the page code, very convenient and quick.
The following will give you an introduction to the use of the code generator, as well as the basic composition of an add, delete, redact and check the page. By learning the following content will help you quickly understand the basic use of this system.
code generator
Create a data table
A migration file for the users table is built in after installing Laravel (if you don't know what the migration file does, refer to the document [Database Migration] (https://learnku.com/docs/laravel/7.x/migrations/7496)). The file path is database/migrations/2014_10_12_000000_create_users_table.php.
Then we run the following command to create this table in MySQL
php artisan migrateAfter running it, you can see that there is already an extra users table in the database, which is structured as follows
CREATE TABLE `users` (
`id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(255) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci NOT NULL,
`email` varchar(255) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci NOT NULL,
`password` varchar(60) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci NOT NULL,
`remember_token` varchar(100) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci DEFAULT NULL,
`created_at` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT '0000-00-00 00:00:00',
`updated_at` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT '0000-00-00 00:00:00',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
UNIQUE KEY `users_email_unique` (`email`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_unicode_ciGenerate add, delete and check pages with one click
{tip} If your development environment is not
windows, please note that to set read and write permissions to the project directory, otherwise there may be unable to generate code.
1. First, open the address http://你的域名/admin/helpers/scaffold to the code generator page.
2.As the data table has already been created, we can directly select the users table from the second drop-down box in the upper left corner of the page, and the fields will be automatically filled with information after selection.
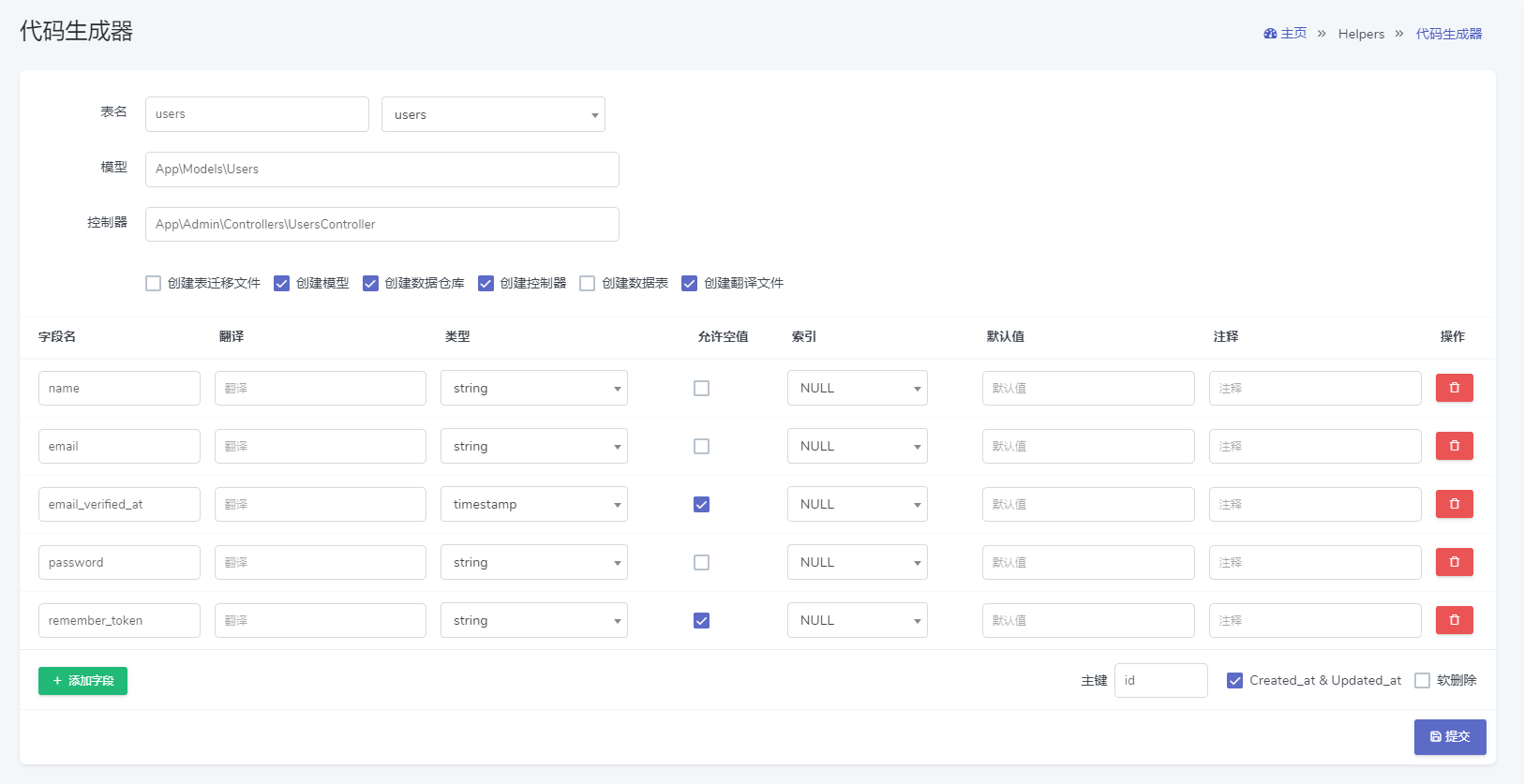
3.Modify the model name to App\User.
4. Since the migration file, the datasheet, and the model file (just use the built-in App\User) already exist, we can remove these three options here.
5.Fill-in field translation
Finally, the result is presented as follows

Finally, click the Create button to create the following file
app/Admin
├── Controllers
│ └── UserController.php # controller
└── Repositories # repository
│ └── User.php
resouces/lang/{当前语言}
└── user.php # language packAdd route configuration
Open the routing configuration file app/Admin/routes.php and add a line to it:
$router->resource('users', 'UserController');At this point, you can open your browser and enter the address http://YourDomain/admin/users to access the page you just created!
Adding the left menu
Open http://YourDomain/admin/auth/menu and add the corresponding menu, then you can see the link to the user management page in the left sidebar of the backend administration page.
Where
urifill in the part of the path that does not contain the route prefix, such as the full path ishttp://YourDomain/admin/demo/users, then fill indemo/users, if you want to add external links, just fill in the full url, such ashttp://dcat-admin.org/.
Menu translation
Append the menu TITLE to the menu_titles index of your language file.
For example, for the "Workplace" TITLE:
In resources/lang/{current language}/menu.php
...
// Replace spaces with _ lowercase and _
'titles' => [
'work_units' => 'Unidades de trabajo'
],Done
Such a simple CURD function on the build is complete, the rest of the work is the depth of building data tables and forms, open app/Admin/Contollers/UserController.php, find the form() and grid() methods, then add the build code.
For more detailed usage, please see data form and data form.
A brief description of the add/drop/remove/check function
To make it easier to understand the basic Usages of the Add/Delete function, the following will give you a brief overview of the code generated earlier using the generator.
Controller
The add/remove/check page code of Dcat Admin is very simple and easy to understand, very developer friendly, requires very little code to build a fully functional backend system, and is very simple, flexible and easy to extend.
Open app/Admin/Controllers/UserController.php can see the following code
<?php
namespace App\Admin\Controllers;
use App\Admin\Repositories\User;
use Dcat\Admin\Form;
use Dcat\Admin\Grid;
use Dcat\Admin\Show;
use Dcat\Admin\Http\Controllers\AdminController;
class UserController extends AdminController
{
/**
* Make a grid builder.
*
* @return Grid
*/
protected function grid()
{
return Grid::make(new User(), function (Grid $grid) {
// The fields here will automatically use translated files
$grid->column('id')->sortable();
$grid->column('name');
$grid->column('email');
$grid->column('email_verified_at');
$grid->column('password');
$grid->column('remember_token');
$grid->column('created_at');
$grid->column('updated_at')->sortable();
$grid->filter(function (Grid\Filter $filter) {
$filter->equal('id');
});
});
}
/**
* Make a show builder.
*
* @param mixed $id
*
* @return Show
*/
protected function detail($id)
{
return Show::make($id, new User(), function (Show $show) {
// The fields here will automatically use translated files
$show->field('id');
$show->field('name');
$show->field('email');
$show->field('email_verified_at');
$show->field('password');
$show->field('remember_token');
$show->field('created_at');
$show->field('updated_at');
});
}
/**
* Make a form builder.
*
* @return Form
*/
protected function form()
{
return Form::make(new User(), function (Form $form) {
// The fields here will automatically use translated files
$form->display('id');
$form->text('name');
$form->text('email');
$form->text('email_verified_at');
$form->text('password');
$form->text('remember_token');
$form->display('created_at');
$form->display('updated_at');
});
}
}Repositories
Dcat Admin building pages do not directly rely on Model, but the introduction of the data warehouse as an intermediate layer, so that the construction of the page is no longer with the read and write data to produce a strong coupling.
Data repository is the specific implementation of the Dcat Admin interface for data add/drop operations, please refer to data repository for more details about Usage.
If your data comes from
MySQL, then you can also useModelinstance directly. To make it easier for you to understand the concept, we've created a data warehouse file here.
We open the just generated file app/Admin/Repositories/User.php, we can see only the following contents, which is quite simple
<?php
namespace App\Admin\Repositories;
use Dcat\Admin\Repositories\EloquentRepository;
use App\User as UserModel;
class User extends EloquentRepository
{
protected $eloquentClass = UserModel::class;
}Language packs
Each controller can generate its own language pack, and the data-grid, data-form and data-detail functions will automatically read the translations.
Let's open the UserController language package file resouces/lang/{current language}/user.php.
<?php
return [
// labels is a custom label translation
'labels' => [
// This is a translation of the page title
'User' => '用户',
],
// Table field translation
'fields' => [
'name' => '名称',
'email' => '邮箱',
'email_verified_at' => '验证时间',
'password' => '密码',
'remember_token' => 'remember_token',
],
'options' => [
],
];