Form Relationships
One-on-one
users table and profiles table generate one-to-one associations via the profiles.user_id field
CREATE TABLE `users` (
`id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(255) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci NOT NULL,
`email` varchar(255) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci NOT NULL,
`created_at` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT '0000-00-00 00:00:00',
`updated_at` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT '0000-00-00 00:00:00',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COLLATE=utf8_unicode_ci;
CREATE TABLE `profiles` (
`id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`user_id` varchar(255) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci NOT NULL,
`age` varchar(255) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci NOT NULL,
`gender` varchar(255) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci NOT NULL,
`created_at` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT '0000-00-00 00:00:00',
`updated_at` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT '0000-00-00 00:00:00',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COLLATE=utf8_unicode_ci;The corresponding models are:
<?php
namespace App\Admin\Models;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
class User extends Model
{
public function profile()
{
return $this->hasOne(Profile::class);
}
}
class Profile extends Model
{
public function user()
{
return $this->belongsTo(User::class);
}
}The corresponding repository is:
<?php
namespace App\Admin\Repositories;
use Dcat\Admin\Repositories\EloquentRepository;
use User as UserModel;
class User extends \Dcat\Admin\Repositories\EloquentRepository
{
protected $eloquentClass = UserModel::class;
}The following code can be associated with a form:
{tip} Instantiating the repository requires passing in the association name defined by the association model, which is equivalent to actively using the
Eloquent\Model::withmethod.
use App\Admin\Repositories\User;
// Note that the repository `User` must be instantiated with `profile` here, otherwise the `profiles` table data will not be associated.
$form = Form::make(User::with('profile'), function (Form $form) {
$form->display('id');
$form->text('name');
$form->text('email');
$form->text('profile.age');
$form->text('profile.gender');
$form->datetime('created_at');
$form->datetime('updated_at');
});If you don't want to use a repository, you can simply use the model
use App\Admin\Models\User;
// Note that the model is used directly here, not the repository
$form = Form::make(User::with('profile'), function (Form $form) {
$form->display('id');
...
});One-to-many
For the use of one-to-many, please refer to the documentation Use of Form Fields - One-to-Many.
Many-to-many
The following is an example of the Role Bind Permissions function of the built-in Role Management module to demonstrate the Usages of many-to-many association models.
Model Role
<?php
namespace Dcat\Admin\Models;
use Dcat\Admin\Traits\HasDateTimeFormatter;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Relations\BelongsToMany;
class Role extends Model
{
use HasDateTimeFormatter;
/**
* 定义你的关联模型.
*
* @return BelongsToMany
*/
public function permissions(): BelongsToMany
{
$pivotTable = 'admin_role_permissions'; // intermediate table
$relatedModel = Permission::class; // Related model class name
return $this->belongsToMany($relatedModel, $pivotTable, 'role_id', 'permission_id');
}
}use Dcat\Admin\Models\Permission;
// Passing permissions when instantiating a repository automatically associates the data of the related model.
// Here we pass in data for permissions associated with the permission model.
$repository = Role::with(['permissions']);
return Form::make($repository, function (Form $form) {
$form->display('id', 'ID');
$form->text('slug', trans('admin.slug'))->required();
$form->text('name', trans('admin.name'))->required();
// The data here is automatically saved in the associated model.
$form->tree('permissions')
->nodes(function () {
return (new Permission())->allNodes();
})
->customFormat(function ($v) {
if (!$v) return [];
// This is a very important step to convert the two-dimensional array found in the database into a one-dimensional array
return array_column($v, 'id');
});
...
});If you don't want to use a repository, you can simply use the model
use Dcat\Admin\Models\Role;
// Note that the model is used directly here, not the repository.
$form = Form::make(Role::with('permissions'), function (Form $form) {
$form->display('id');
...
});The final result is as follows
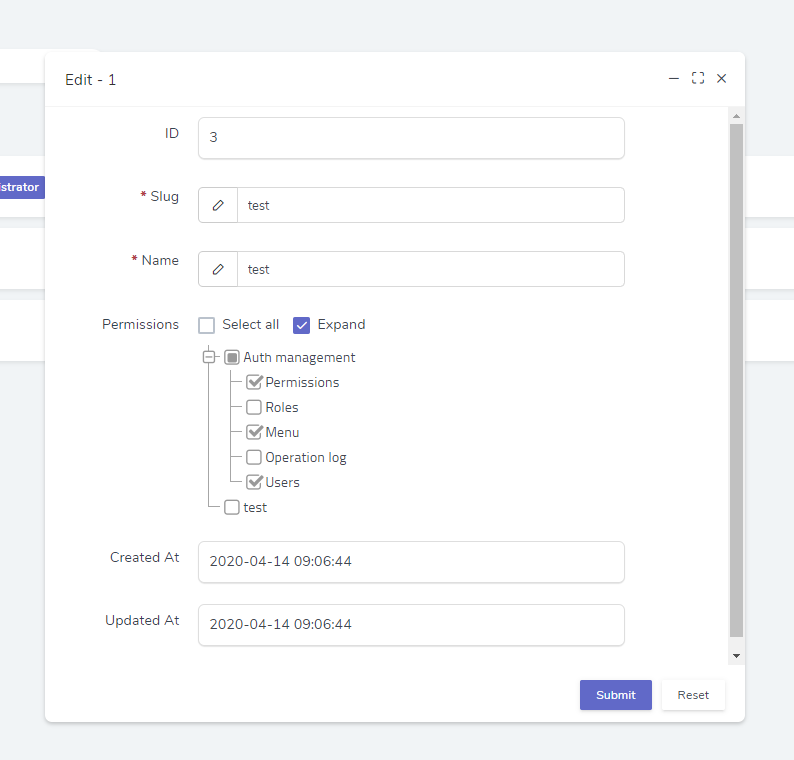
Associated model name is camelCase style
If the name of your associated model is named camelCase style, then the use needs to be converted to snakecase style naming
for example
class User extend Model
{
public function userProfile()
{
return ...;
}
}use
return Form::make(User::with(['userProfile']), function (Form $form) {
...
// Note that you must use snake_case style naming here, otherwise the edited data will not be displayed.
$form->text('user_profile.postcode');
$form->text('user_profile.address');
});